An overview of Industry 4.0 solutions developed within the AUTOWARE project. You can also download the Technology Catalogue in PDF here.
1.0 Fog Computing Solution

The Fog Computing solution is an industrial IoT solution designed to converge and connect automation systems. It provides an open, flexible platform that reduces costs and delivers new value for machine builders, system integrators and plant operators. It can collect, store and analyze machine data and run multiple functions on one device.
2.0 Integration of Fog node
The open CPPS platform (i.e. fog node) will be integrated as a central station, where the configuration of the open platform will be performed with the usability enablers for programming and controlling the fog node. The node will act as a central point, where the different applications (e.g. data management) will be hosted on.
3.0 Smart Data Distribution
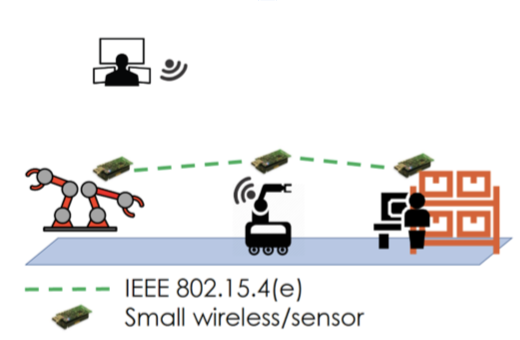
Novel smart data distribution technological solutions which cooperate with cloud-based service provisioning and communication technologies. The solutions presented in AUTOWARE determine when it is appropriate to move data towards locations where services can be provided.
4.0 Semantic Workflow Modelling
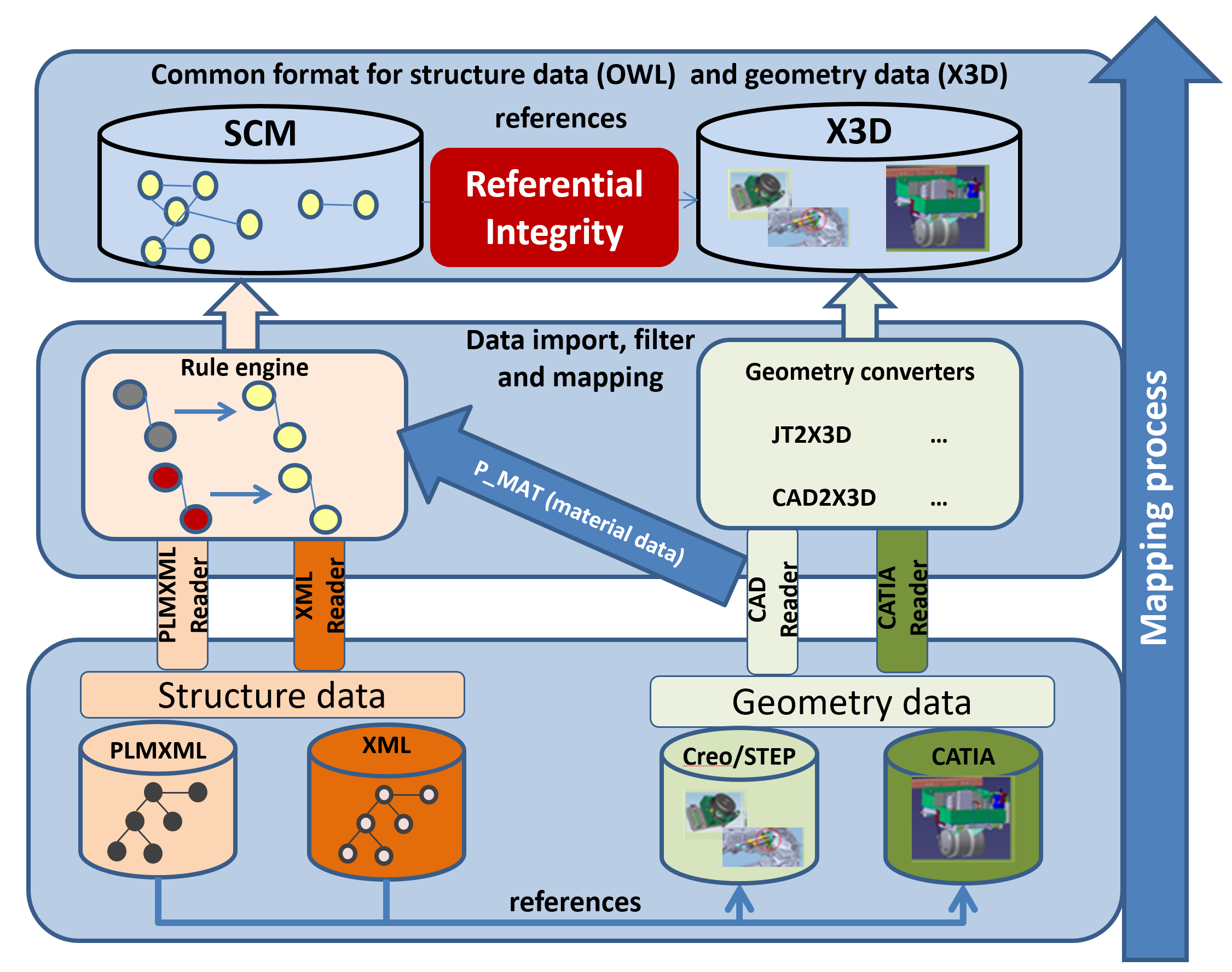
The semantic workflow modelling service foresees to make existing product engineering and production planning data available for secondary use, namely for cooperative assembly tasks. By retrieving product engineering data (i.e. 3D CAD files) and production planning data (i.e. structured textual data describing the manufacturing execution and the assembly process) from a company’s Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) system, the service will generate a semantic description of the assembly process incorporating the 3D representations of the assembly steps.
5.0 Dual Reality Modelling
The dual reality modelling service allows enriching dynamic virtual environments with virtualized physical production environments (Augmented Virtuality). In doing so, it uses 2D/3D sensor data and relies on a continuous mapping of the current state of the real world onto the virtual world and vice versa.
6.0 Sensor Processing

A 3D optical sensor based on structured laser light (line sectioning and space-time analysis) that supports two different scanning modes: the first for coarse and fast scanning of larger parts and the second for slower but precise scanning at marked positions. The technology includes an initial self-configuration of the system and is essential for robot trajectory and view planning that enables autonomous 3D scanning.
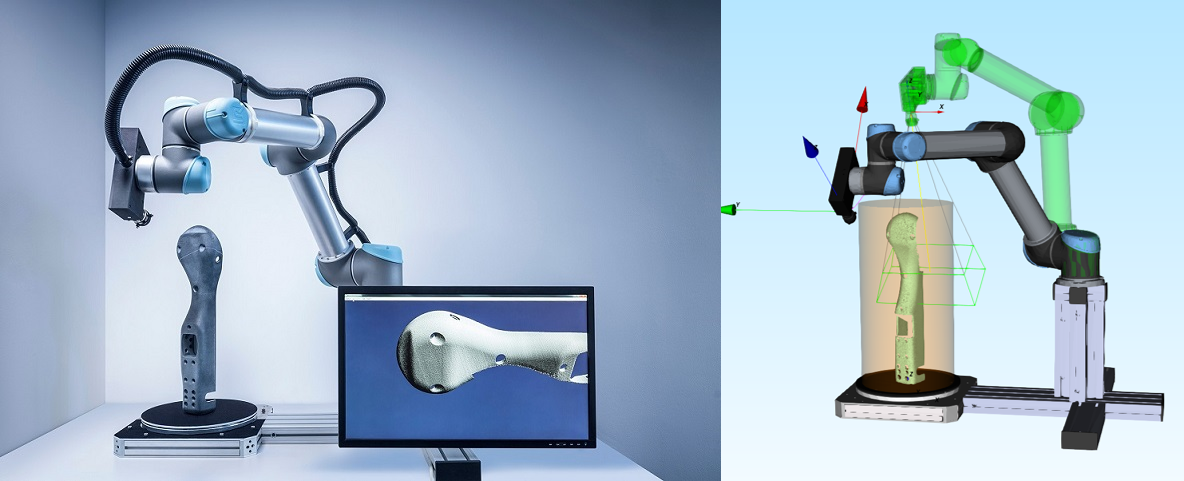
7.0 3D Object Retrieval & Recognition
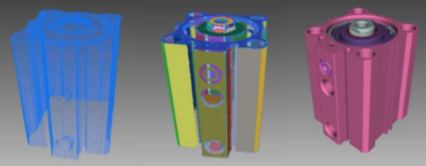
Many existing shape representations describe actual shapes, with visual and material properties. However, applications often require enhanced shape properties. For example, shape structure information, such as segmentation or label information, can help to relate the parts of a shape to each other. The 3D Object Retrieval and Object Recognition service can use engineered but also learned features in order to classify and recognize 3D objects.
8.0 3D Quality Control
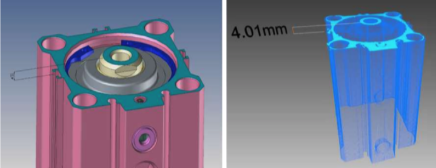
With this service, the user is relieved from doing a manual check of dimensions after the completion of assembly steps. The quality control service requires an annotated 3D CAD model with measurement details and a 3D point cloud of the real object. The service automatically retrieves the measurement details, which are involved primitives e.g. planar segments, the expected distance between the primitives and allowed tolerances.
9.0 Neutral Cognitive Digital Automation Process Experimentation Infrastructure
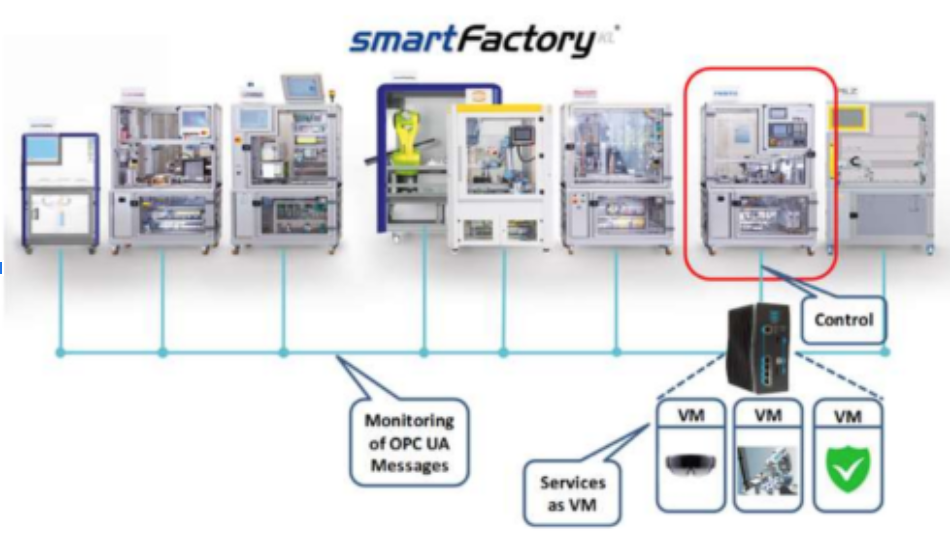
In the neutral test factory SmartFactoryKL, the fog node is attached in the edge layer. This is integrated with the infrastructure of the individual production modules, more precisely with the industrial M2M (Machine-to-Machine) communication protocol according to the OPC (Open Platform Communication) specification, with which the production modules communicate with the higher-level MES (Manufacturing Execution System) system. These transmitted messages can be evaluated and processed in the fog node.
10.0 Active Product Memory

The Active Product Memory services as an extension of the common product memory used in SmartFactory. This consists of an RFID chip attached to the test product.
11.0 Machine Learning

Deep learning based computer vision - ROBOVISION has configured deep learning systems and associated tools to create novel machine vision systems, which are applied in the use-cases.
12.0 GpflowOpt

IMEC has developed GpflowOpt, a novel Python framework for Bayesian optimization, which can be viewed as a modern spin-off of the widely used SUMO-toolbox.
13.0 Programming by kinesthetic teaching
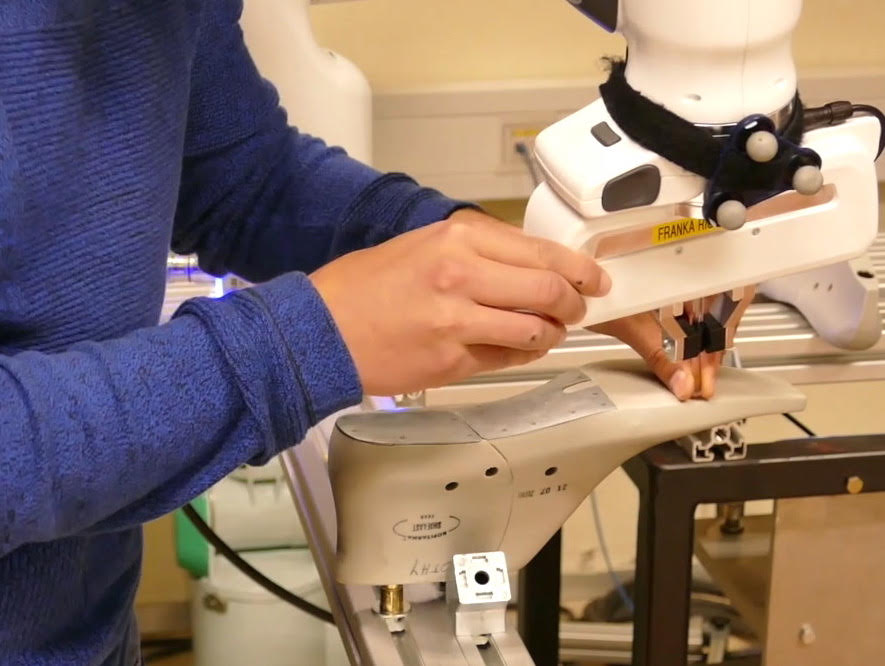

Programming by kinesthetic teaching allows for specifying and editing complex robot trajectories in a natural, user-friendly way. With the help of incremental learning, only certain parts of the trajectory can be changed. Using this technology does not require any special knowledge of robotics.
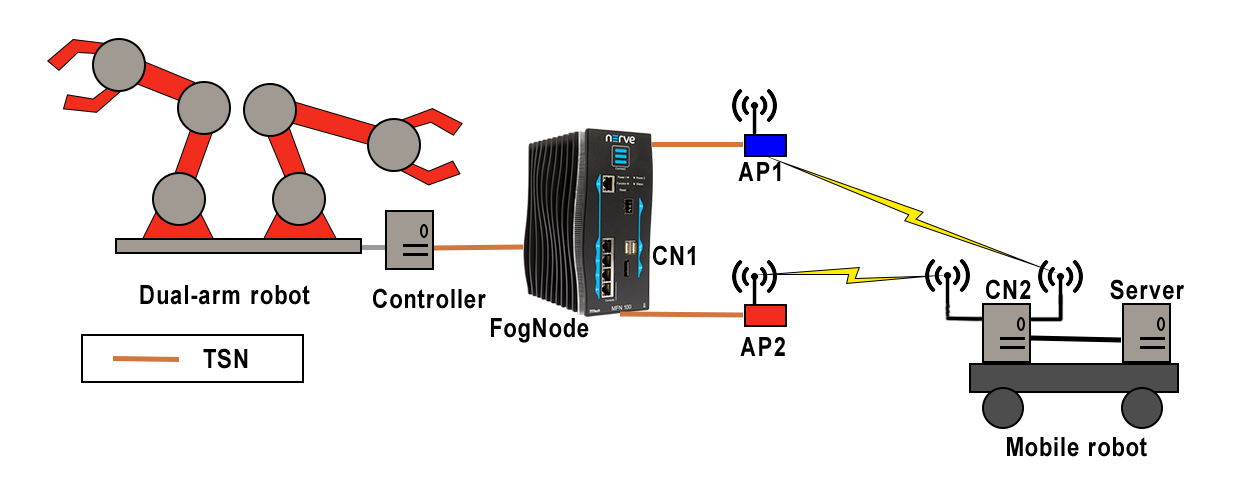
14.0 Reliable wireless networks for Industry 4.0

This service provides reliable and robust wireless communications for the support of mobile industrial applications. This service exploits diversity and redundancy to increase the reliability of the wireless communication between a fixed robot (or a controller) and a mobile robot.
15.0 Digital automation

Digital automation solutions put stress on safe and secure operation of future workplaces. Traditional certification approaches are not well suited for modular production lines and collaborative reconfigurable robotic cells. Existing standards need to be adapted to the new 4.0 reality. Fast and cost-effective validation, verification and certification of new developed technologies for manufacturing 4.0 is a must for their integration in a factory.
